Is there a distinctive Jewish perspective on revenge? The question obviously bears on the contemporary world in pressing ways. Revenge is a complex concept about which psychology, anthropology, philosophy, law and other fields offer important perspectives. But one way to answer it is to turn to the history of Jewish life, literature and culture. Here we can find a distinctive feeling and action on a matter that is as old as humanity, a human feeling in response to an injury or harm, and one closely bound to ideals of justice. The mid-20th century in particular, a formative period of Jewish and Israeli existence, has much to tell us about the relationship between violence, revenge, justice, memory and trauma in Jewish and Israeli life.
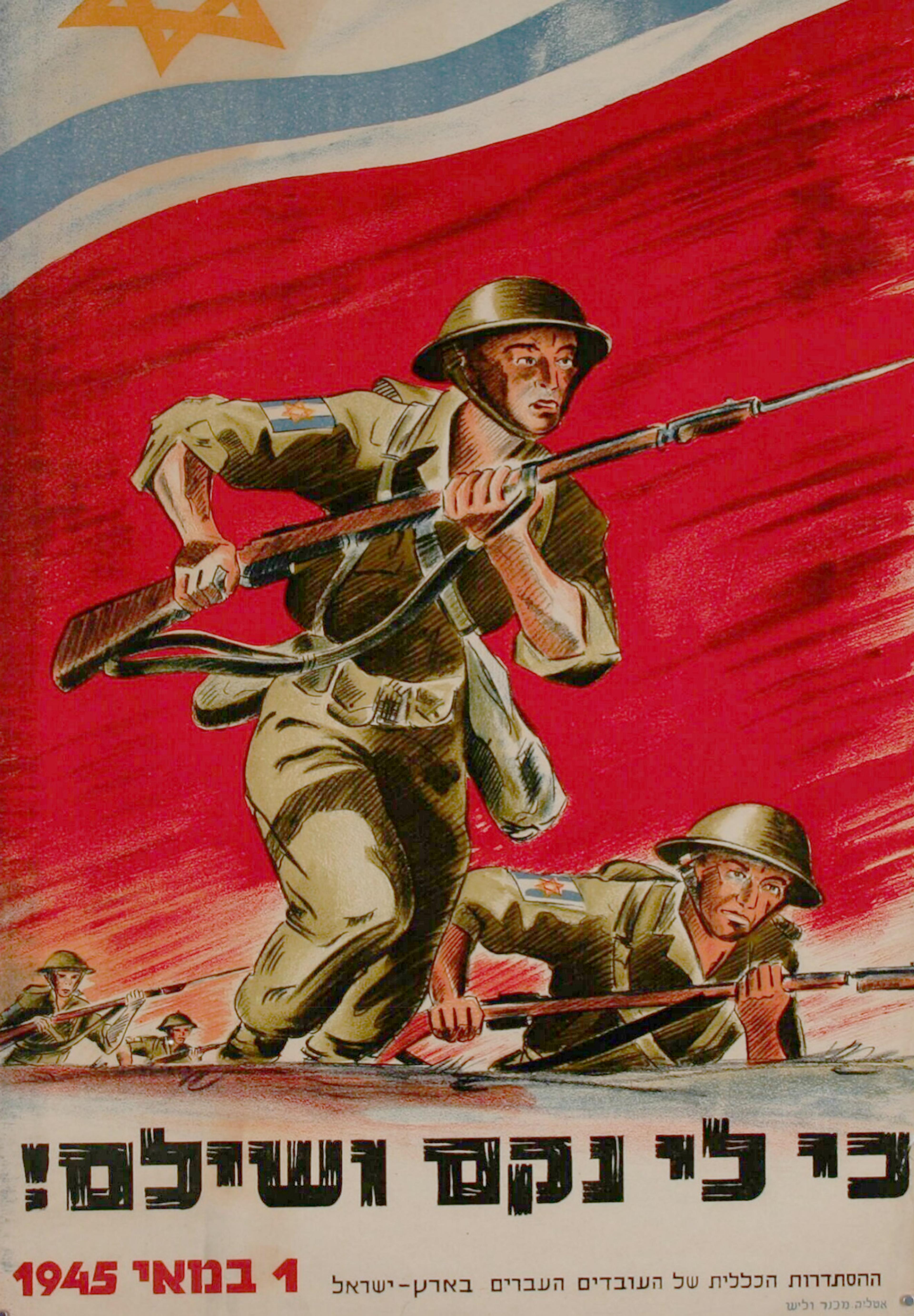

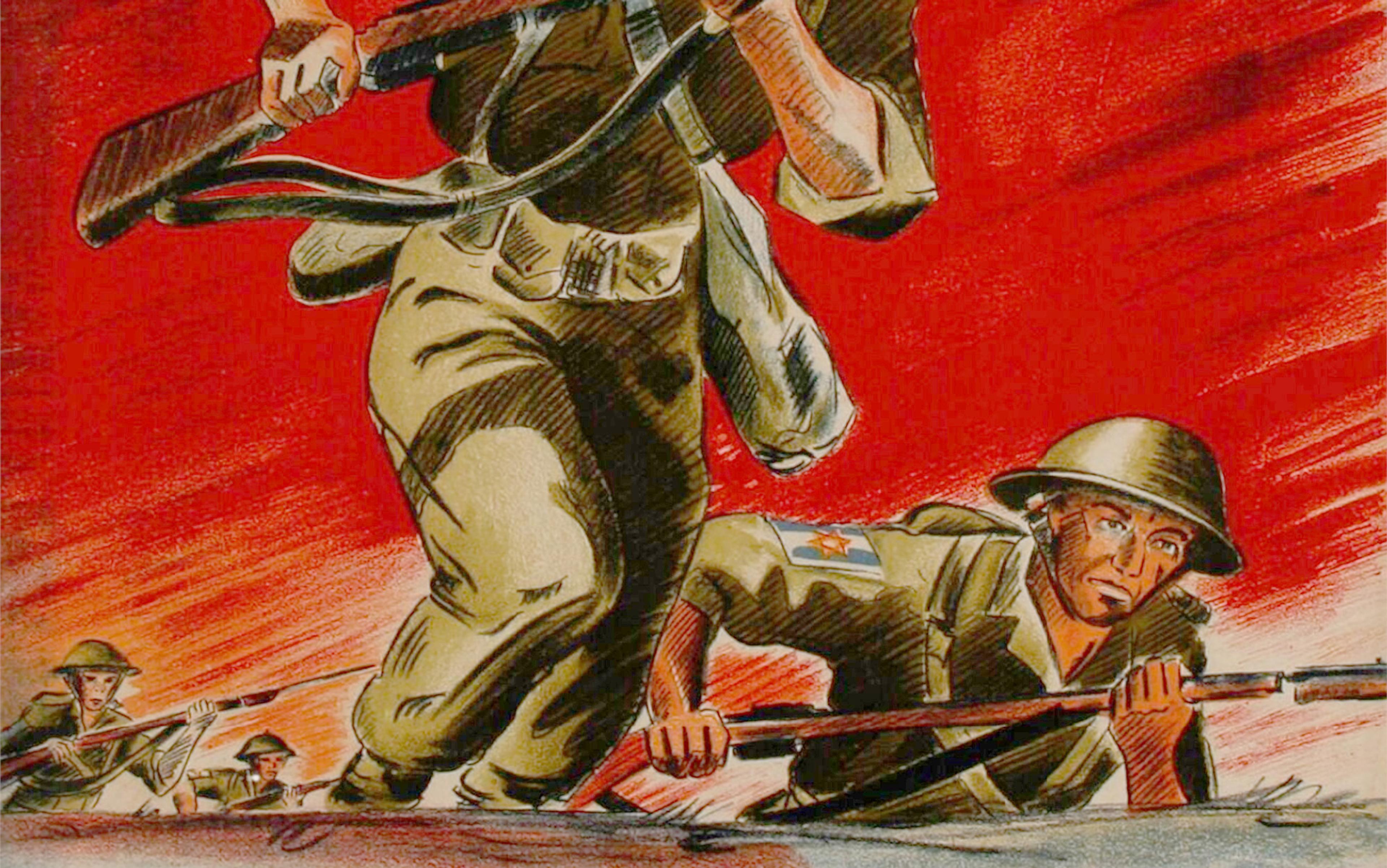
‘To be My vengeance and recompense’ (translated from Hebrew; Deuteronomy 32:35): recruitment poster by Ernest Mechner and Otte Wallish, for the Jewish Brigade in Palestine, 1945. Public domain. Courtesy the Eri Wallish Collection at the National Library of Israel
Since 7 October 2023, nekama (‘vengeance’ or ‘revenge’ in Hebrew) has emerged as one of the key words in Israeli public life. We’ve heard discussion of nekama from the government, the Knesset, the media, the army, social networks, synagogue bulletins, and in popular culture. Perhaps the most immediate and relevant invocation came on the same day of Hamas’s attack, from the Israeli prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu, who declared: ‘The IDF will immediately employ all its power to destroy Hamas’s capabilities. We will strike them until they are crippled, and we will avenge with full force this black day they inflicted upon the State of Israel and its citizens.’ In the past few months, there were many poems on revenge written by Israelis, some of them IDF soldiers.
Like many basic concepts, there is really no consensual definition for revenge, or for its relation to near-synonyms such as ‘vengeance’ or even ‘retaliation’ and ‘retribution’. It seems certain, though, that revenge is connected to the realm of emotions and affect, for there can be a desire or a fantasy of vengeance without actualisation. But, of course, it also describes actions. The thirst for revenge animates much of the world of tragic literature, and it is a common element in art, theatre and cinema. Revenge begins within the family or tribe but it expands beyond, to town or sect or king or nation.
Revenge has a distinctive and dynamic relationship to time: it is caused by an act of wrong that happened in the past as an explanation for the present moment, but it is also directed towards the future. Austin Sarat, a scholar of law and politics, explains that vengeance attempts, consciously or not, to reenact the past, as it is ‘one means by which the present speaks to the future through acts of commemoration’. The fact that vengeance looks backwards and seeks to cancel out past actions is one reason why the relationship between revenge and justice is complex. Revenge can indeed be the opposite of justice, a product of utter despair, a kind of empty and final gesture toward restoring one’s shattered self-respect. The scholars Susan Jacoby, Martha Minow and Sarat have all written important work trying to better understand and clarify the connection between revenge and justice. They all would concede that there is an understanding that ‘revenge is a kind of wild justice,’ as Francis Bacon wrote in his essay ‘Of Revenge’ (1625). Most modern systems of law claim authority by distinguishing themselves from revenge, though conceding that feelings for revenge cannot be eradicated. Scholars of politics and law seem to agree that there is no place for revenge in modern international relations. Here too, however, as the scholar Jon Elster has shown, revenge persists, often concealed under more technical and dispassionate terminology about state or national interests.
In the Israeli Jewish psyche, 7 October passes through a filter of collective trauma centred on the Holocaust
Jewish sources give us many, sometimes contradictory, voices on nekama. Many biblical texts prohibit vengeance by human hands, as well as collective Jewish vengeance, although there is an exceptional case of revenge against the people of Amalek, biblical enemies of the Israelites. In post-biblical work, vengeance assumes the form of a divine promise that the redemption of the people of Israel will come to fruition when God enacts revenge upon their enemies. This version of nekama is a kind of eschatological prophecy. The only act of vengeance in the Bible with some elements of the noble, albeit dangerous, tragic revenge we find in the classical Greek literature, is the story of Samson in the book of Judges avenging himself on the Philistines in ancient Gaza. It is not a surprise that some of the poems and popular songs about revenge are focused on Samson.
The violence of the 20th century has profoundly shaped modern and contemporary Jewish views of vengeance. Violence against Jewish people in the past century includes not just the Holocaust but also the Kishinev pogrom in the Russian Empire, the massacre of Jews after the First World War in Ukraine by those who blamed them for the turmoil of the Russian Revolution (which led to the assassination of the Ukrainian politician Symon Petliura by Sholem Schwarzbard), the massacre of Jews in 1929 in Palestine, and more.
Since 7 October, the Holocaust and its memory has re-emerged as particularly central to Israeli and Jewish thinking on vengeance. Immediately following the exposure of the horrors of the Hamas attack, Israeli Jews invoked memories of the Holocaust. Historical basis for such comparisons aside, in the Israeli Jewish psyche, 7 October clearly passes through a filter of collective trauma centred on (but not limited to) the Holocaust. Indeed, the popular perception of Israel, its need for security, and its national narrative of ‘from Holocaust to rebirth’ are inseparable from trauma. Nor is it possible to disentangle the link between the Holocaust and the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, which was both Israel’s War of Independence and the Palestinians’ Nakba (‘catastrophe’).
In an important 1996 paper, the American Jewish philosopher Berel Lang asked: what is vengeance and revenge in Jewish consciousness worldwide? What about in the Yishuv (the Jewish community in pre-state Palestine), during and after the Holocaust? How did the desire for vengeance, Lang wanted to know, influence the memory of the Holocaust? Lang wondered because there were few attempts (and even fewer successful ones) of revenge by Jews following the Holocaust. It would be wrong to say there was no discussion, however. One needs to understand ways in which, during and following the Holocaust, Jewish desire for vengeance was displaced from direct acts against Nazis or Germans to other, less direct phenomena: for example, the Nazis and Nazi Collaborators (Punishment) Law enacted by the State of Israel in 1950 to bring to court SS soldiers and Nazis; and people such as Simon Wiesenthal, known as ‘Nazi hunters’, who tried to gather information and track down Nazis around the word. The desire for revenge and retribution was also part of the divisive and robust debate around whether Holocaust survivors should accept payment from Germany and around the Reparations Agreement between Israel and the Federal Republic of Germany, which was signed in September 1952.
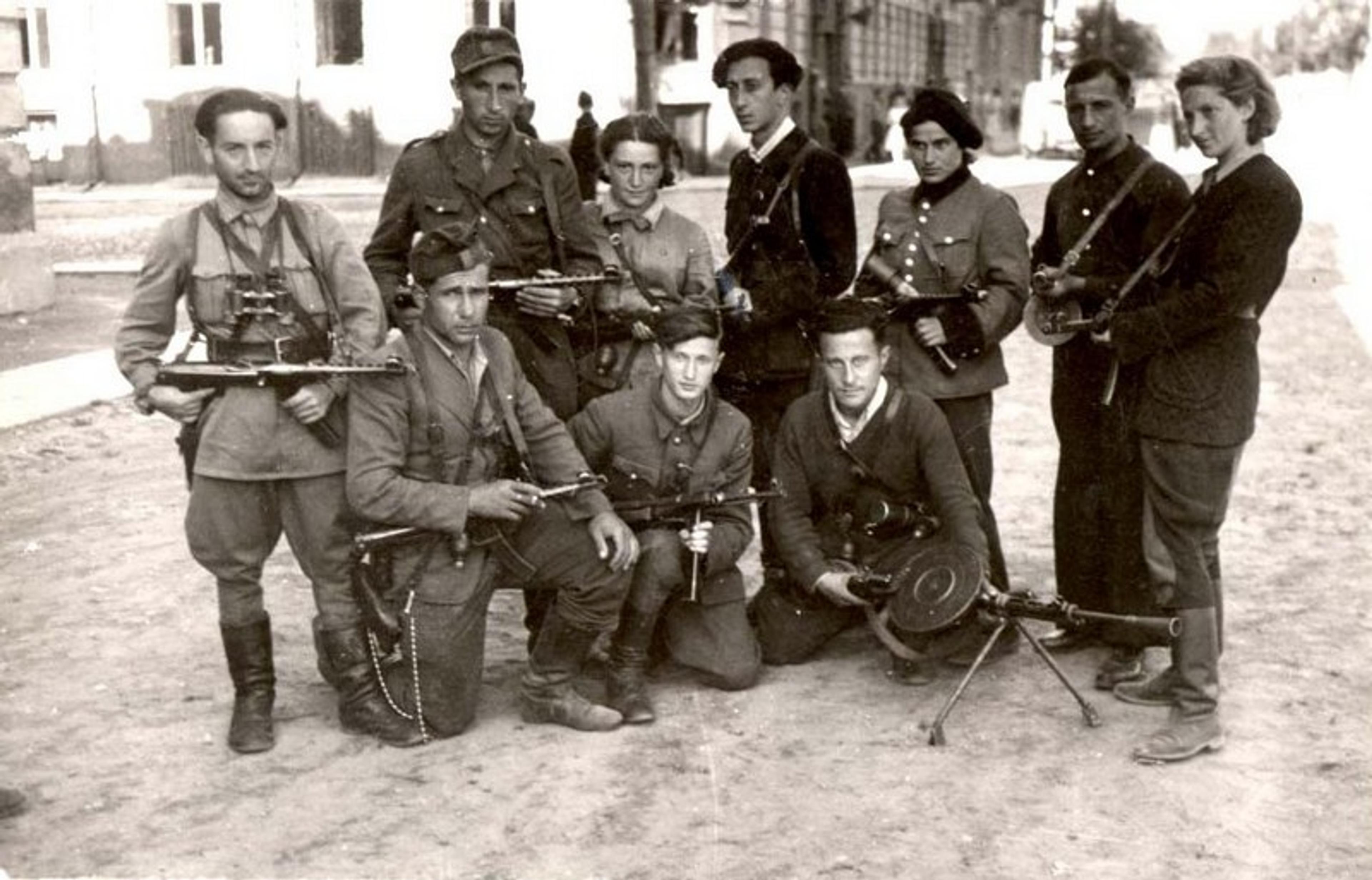

Abba Kovner (c, back row) with partisans in Vilnius in July 1944. Courtesy Yad Vashem archives.
The ‘Avengers’, a group led by Abba Kovner, a partisan from the Vilna ghetto, are central figures in post-Holocaust Jewish revenge. After the Second World War, the Avengers targeted Germans. Dina Porat’s book Nakam: The Holocaust Survivors Who Sought Full-Scale Revenge (2022) tells their story. An Israeli-German co-produced film, Plan A (2021), is also about the Avengers. This renewed interest in them may create the impression that they were unique, but that is not the case. Kovner, who wished to avenge by killing as many as 6 million Germans, is an extreme figure, but he is not exceptional. As we will soon see, Kovner’s writings and ideology express central concepts in Jewish and Israeli culture that emerged after the Holocaust and in the years surrounding the founding of Israel.
Poets, writers and journalists in Europe and the US discussed Jewish revenge, its possibilities and limits
Even before the full dimensions of the Nazi extermination of European Jewry had been fully revealed, Jews wrote about and engaged in profound debate on the question of revenge. Most of that writing is in Yiddish. Yiddish is the historic language of central and eastern European Jewry, dating back 1,000 years. It is a Germanic language, but fuses Semitic components, as well as Slavic and other elements from where Jews lived. It is a diasporic language. Zionism and, later, Israel rejected it in favour of modern Hebrew as the national language. Despite the fact that most Zionists were Yiddish speakers, it was the language that must be forgotten in the making of Israeli society and culture.
In Kraków, a few months before he was murdered by the Nazis in 1942, Mordechai Gebirtig wrote ‘A Day of Revenge’, a poem in Yiddish that was also put to music. The Soviet poet and member of the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee Peretz Markish wrote ‘To the Jewish Soldier’ (1943), a Yiddish poem in which the speaker declares: ‘The blood on every road cries out, vengeance.’ Poets, writers and journalists in Europe and the US discussed questions of Jewish revenge, its possibilities and limits. Jacob Glatstein wrote ‘Revenge, Revenge, and Revenge!’ (1944), an article where he considers revenge by European Jews as a desire and principle of justice, while acknowledging, due to their murder by the Germans, its impossibility.
In the mid-1950s, discourse of revenge in Yiddish faded away but, as Lang pointed out, the aspiration did not disappear; it transformed. For example, it shifted towards a search for Nazis in hiding, the Nazis and Nazi Collaborators (Punishment) Law, and fuelled debates about reparations from Germany to Israel. It also moved into other phenomena that generally do not seem directly related to revenge, such as the ‘Stalags’ – a popular, short-lived genre of Holocaust pornographic Hebrew books in Israel that flourished in the 1950s and early ’60s.
During and after the Second World War, a parallel but distinct discourse about revenge also arose in Hebrew, an ancient language that was revitalised to become a key aspect of Zionism. The Hebrew-language works came from the poets Uri Zvi Greenberg and Nathan Alterman, who immigrated to Palestine from Europe, and from younger writers born in Palestine. Alterman, the most influential mainstream Hebrew poet of the 1940s, examined vengeance and revenge in his books The Joy of the Poor (1941) and Poems of the Plagues of Egypt (1944), and in poems published in the Labor Zionist newspaper Davar. For example, Alterman wrote ‘A Prayer of Revenge’ in which the speaker seeks divine assistance in carrying out their vengeance:
And what does your servant, supreme Father, seek?
Only to stretch out his hand to their necks …
And they said: Let there be vengeance.
Do not tell him: Have mercy! Do not call him: Forgive!
Do not forget, do not forget what they did to him.
Alterman wrote this poem during the Second World War, before Hebrew readers in the Yishuv knew exactly what was going on in Europe. It expressed the sense of vulnerability and frustration, turning to God as a father with a wish for revenge as expressed in ancient Jewish texts, but without making clear who should enact the vengeance.
Vengeance was a motivational force in the decision of young Jewish soldiers who enlisted to serve in Europe
By the end of the Second World War, writing about vengeance in Hebrew had taken on a new significance. A million and a half Jews fought in the armies of the Allied Powers. Writing in Hebrew, however, focused on the 30,000 Jews from the Yishuv who volunteered to fight alongside the British army, especially the Jewish Brigade, numbering about 5,000 men. The Brigade fought on the Italian front in March-May 1945, but most of its activity followed the war. Its significance lay in the fact that the language, flag, symbols and anthem of the Jewish Brigade were Hebrew. Brigade people were active in the paramilitary units of the Haganah and Palmach. The anthem of the Jewish Brigade was written by the poet Yaakov Orland:
Our blood is flowing like a river and fire
Our covenant is calling – for vengeance!
We swore, we swore, brothers in arms,
That none shall return in vain.
Twenty years later, the writer Hanoch Bartov, a Brigade member, wrote in his autobiographical novel Pitzei Bagrut (1965; later translated and published in English as The Brigade) these words, spoken by the protagonist Elisha Kruk:
Not much: a thousand burnt houses. Five hundred dead. Hundreds of raped women … We’re here to redeem blood. One wild Jewish vengeance. Once, like the Tatars. Like the Ukrainians. Like the Germans. All of us … will enter one city and burn, street after street, house after house, German after German.
It is clear from these texts that vengeance was a motivational force in the decision of young Jewish soldiers who enlisted to serve in Europe as part of the Brigade (some of them had lost family members in Europe), and that at least some of these soldiers expected to be able to take revenge on Germans.
In 1945, Brigade soldiers met for the first time in northern Italy with people of the She’erit Ha-pletah (‘the Surviving Remnant’), Holocaust survivors and refugees, as well as partisans and ghetto fighters. Some of the She’erit Ha-pletah had been active in Zionist youth movements even before the war. Kovner had just gathered in Lublin, Poland, about 50 young men and women who had a burning desire to take revenge against not only the Nazis but the entire German people. The details that captivate the imagination of many in the story of Kovner and the Avengers – ‘Plan A’, the killing of 6 million Germans by poisoning the water supply of major German cities, and ‘Plan B’, the killing of SS officers and Gestapo officials who were imprisoned in prisoner camps – are less important. More significantly, Kovner stands as a bridge between Holocaust survivors, most of whom spoke, read and wrote in Yiddish, and people from the Brigade, who represented the Hebrew Zionist Yishuv. It is the latter who shaped the ethos of the State of Israel, and some of whom later served in senior roles in the IDF and Israel’s security apparatus. This is a significant shift towards revenge as part of the Zionist discourse of military power in the context of conflict with Arabs in Palestine in the years around 1948 and the establishment of the State of Israel.
In 1944, the Zionist leader and future Israeli prime minister David Ben-Gurion spoke about ‘revenge for the spilled blood’ of European Jews as one of the reasons for establishing the Brigade. By November 1945, Ben-Gurion – the pragmatic politician and statesman – concluded that, after the war, revenge was ‘a matter of no national benefit’ because killing Germans will not bring back those who were murdered, and he silently disavowed Kovner’s plans. Nonetheless, Kovner and the Yishuv formed a significant relationship. Kovner’s family and several members of the Avengers settled in Kibbutz Ein ha-Horesh in March 1946, and Kovner became an influential figure around 1948, when, amid war, the IDF gradually began to form.
As the scholar Uri S Cohen has shown, in the struggle with the Palestinians and Arab states, Hebrew writers and poets, mostly men born in Palestine and known as the Palmach Generation, wrote a great deal about revenge. For example, the novelist Moshe Shamir wrote a series of novels between 1947 and 1951, each featuring a theme of personal and collective revenge, not against the Nazis or Germans, but against Palestinian Arabs. The desire for revenge against Palestinians during the 1948 war coincided with an important transition away from militias such as the Palmach, towards a regular Israeli army. Revenge became a central part of Hebrew militia culture. Nahum Arieli, a commander in the Palmach, wrote about the death of his friend and Shamir’s brother Eliyahu: ‘To gather strength, to organise quietly, and to go out again … to avenge our Eli!’ Instead of Nazis or Germans, revenge against the Arabs served as the emotional core of the literature of the 1948 war. During ‘Israel’s border wars’, between 1949 and 1956, which were essentially a chain of ‘reprisal operations’ dominated by the Commando Unit 101, vengeance remained a driving force. From these conflicts emerged well-known fighters who loomed large in the Israeli and Jewish public imagination, including Ariel Sharon and Meir Har Zion.
The desire for revenge had found an outlet against another group that was causing feelings of threat: the Palestinians
Kovner did not fight in the 1948 war. Instead, he served as a ‘cultural officer’ of the Givati Brigade. Kovner named the commando unit of the Givati Brigade Shu’alei Shimshon (‘Samson’s Foxes’) after the biblical Samson and his foxes who carried the fire of vengeance against the Philistines. In his new role, Kovner wrote ‘battle pages’ with rhetorical force:
With love and with hatred, for the sake of our homes, for the sake of the lives of our children, and the eyes of eighty generations are watching us, and six million souls … call out to us from the earth: Rise, the great revenge – free Israel, forever!
Kovner is many things, a historical and political figure, a writer, but he is also a symbolic and transitional figure because his words and actions during the 1948 war show a profound change: the transition from revenge as a response to the Nazis and Germans to revenge against Arabs. As Netiva Ben-Yehuda, an Israeli author, editor and radio broadcaster who was a commander in the Palmach, wrote years after about the 1948 war: ‘We fixed our guns on the Arabs, we pulled the trigger … and we imagined to kill Nazis.’
For Lang, the displacement ‘at one farther remove’ of revenge against Nazis or Germans onto Arabs was ‘a form of demonisation and aggression’. Lang maintained that it could not be accounted for by the real threats Israel had faced, and that it required ‘disfigured representations’ of Arabs. In its people’s ‘emergence from [the] powerlessness’ of the Holocaust, the State of Israel had found in the Arabs an ‘available target’ for revenge. The Israeli psychologist Dan Bar-On, who for many years studied the relations between Israelis, Germans and Palestinians, suggested that the desire for revenge had found an outlet against another group that was causing feelings of threat: the Palestinians, who are perceived as ‘the natural continuation of the previous aggressor’.
There are key differences between what people who did not directly experience the horrors of the Holocaust wrote in Hebrew, and what survivors and refugees who arrived in Palestine/Israel after 1945 wrote in Yiddish. Avrom Karpinovitsh’s Yiddish story ‘Don’t Forget’ (1951) deals with a Jewish soldier who arrives in Palestine from a displaced persons camp directly into the battles of 1948, after being conscripted as part of the ‘foreign recruitments’. In Karpinovitsh’s story, the unnamed soldier finds himself alone and disoriented after capturing a Palestinian Arab. The Jewish soldier has no idea what to do with the captive and, in the absence of a common language, they cannot communicate. The captor is terrified but hopes that, if he manages to bring the captive to his commander, he will finally be able to transform himself from a disgraced refugee into a ‘real Israeli soldier’. His plan fails because he cannot find his way in the unfamiliar terrain and the oppressive weather.
The climax of the story occurs when the captive takes advantage of the soldier’s moments of confusion and picks up a stone. At that moment, the prisoner speaks for the first time and says something, presumably in German: ‘You have no right, I am a war cap[tive].’ Instead of considering the status of prisoners of war, the Jewish soldier feels threatened, and his memory leads him to a particularly traumatic moment:
The captive’s hoarse murmur transported him back once again to the earthen hut in the middle of the forest where he and his mother hid after fleeing the ghetto – ‘Don’t forget, my child, to say Kaddish for your dead father. Even if, God forbid, you remain alone, don’t ever forget.’
The Jewish soldier remembers how the Nazi killed his mother brutally in front of him and the cry of ‘Don’t forget’ that he still hears. Now, when he is confronted with the Palestinian captive, he contemplates:
This is him … That same pale face of the Angel of Death. The same cold vicious glance, there in the forest, and here – with the stone. The same killer’s hands with the long fingers that strangled her so powerfully as she cried out … and perhaps this is not the same man?
The protagonist is disgusted with the act of violence and the futility of displaced vengeance
In this harrowing story, it is hard to discern reality from the imaginary. In this traumatic moment, ‘don’t forget’ translates into a call for revenge in the new reality. The Holocaust survivor who becomes an Israeli soldier, in his imagination, turns the Nazi into a Palestinian and brutally kills the captive. At that moment,
Something gnawed at his heart: an unsatisfied thirst for revenge … Suddenly, the picture of his mother, fresh-faced on a Friday evening, surfaced before his eyes. She would never come back to him, not even with a thousand deaths of this murdered man.
The protagonist is disgusted with the act of violence and the futility of displaced vengeance.
The story does not provide answers but only questions. Karpinovitsh’s ‘Don’t Forget’, written in Yiddish by someone who was close to the events of the Holocaust, gives voice to refugees who immigrated to Palestine/Israel and were thrown into the 1948 war, trying to assimilate into Israeli culture immediately after experiencing the horrors of the Second World War. The story asks questions about the power of traumatic memories, and the relations between memory and the desire for revenge as ‘wild justice’, but also reflects on the act of displaced and violent revenge as ultimately futile and harmful.
By the end of the 1948 war, hundreds of thousands of Palestinians became refugees, mostly fleeing to nearby Arab countries. The armistice agreements between Israel and its neighbours drew the new borders for the State of Israel, but violent incidents around these borders were quite common. In October 1953, members of an Arab paramilitary commando group killed a Jewish family in the town of Yehud, which had been depopulated of its Palestinian residents in the 1948 war. Before the ‘reprisal operation’ that occurred after the attack on Jews, Sharon, as commander of Unit 101, wrote in the operation’s orders that the objective was an ‘attack on the village of Qibya, its temporary conquest, and maximum damage to the population with the aim of evacuating the villagers from their homes … by damaging a number of houses and killing residents and soldiers in the village’. Although Sharon’s comment does not mention the word nekama, it must be understood as a vengeful act that became part of the norms for Unit 101. During the operation, IDF soldiers blew up 45 houses in the village with their occupants, and 69 residents of Qibya, mostly women and children, were killed. Many Yiddish writers were shocked and responded to the massacre. In a New York Yiddish journal in 1964, Glatstein wrote:
Anger, revenge, smoke.
A small camp with murder in their eyes.
Girded with bow and arrow,
In treachery of night …
Glatstein, who’d written about Jewish revenge against the Nazis and Germans in 1944, is furious about the Israeli displacement of vengeance.
The Yiddish-Israeli writer Yossel Birstein also wrote about Qibya in the story ‘Between the Olive Trees’ (1954). Most of the story revolves around Hasan, an elderly Palestinian in the olive grove near ‘the ruined huts from the last war’. At the climax of the story, a soldier stops Hasan and declares his authority as a representative of the armed forces. In the confrontation, a bag of oranges falls from his donkey, and while Hasan bends down and goes ‘on all fours’ to pick them up, the Israeli soldier towers over him and their gazes meet, when the soldier sees Hasan ‘like a pile of rags’. In this brief encounter, the Jewish soldier hears the subdued cry of Hasan, and ‘is confused’ by it. The confusion surely arises from his memory of persecution in the Holocaust, which surfaces and moves the soldier. Hasan, the elderly Palestinian, and the Israeli soldier in the story are both figures who have repressed painful and traumatic experiences that occurred during the Holocaust and the Nakba. The story depicts a Jewish refugee or survivor who, in order to fulfil his new role as an Israeli soldier in retaliatory and vengeful actions like Qibya, is required to see the Palestinian as a threatening enemy and, even worse, as a dehumanised being. Birstein handles the matter with delicacy, but readers can sense in the story the danger of the vengeance’s displacement from Europe to Israel/Palestine, a displacement that leads to dehumanisation.
As we can see, during and after the Holocaust, European Jews clearly desired revenge, and this feeling persisted for many years, often in complex, displaced ways. The problem raises the question: can the impulses towards revenge be directed to less violent and destructive channels in post-Holocaust Jewish culture? Following in the footsteps of Hannah Arendt’s discussion of the topic in the book The Human Condition (1958), Lang explains a fundamental difference between two possible responses to acts of wrong or injustice: forgiveness and revenge. In terms of temporality, forgiveness is effectively the attempt to erase what happened in the past, and therefore to try to let a painful memory go. Revenge is different because, in the desire to avenge wrong acts, the past must persist. Because vengeful desire is directed towards the future, it resonates in the present and contributes to the memory of the past by not letting it go. We must understand that memory is something that we choose, too; it requires construction and cultivation. It is not just a natural attribute or a reservoir waiting to be filled. Thus, one can understand a human sense of the need for revenge as a persistent desire for justice and, therefore, as an element to foster memory, both personal and collective, part of a Jewish imperative to ‘never forget’ what happened in the Holocaust.
Rachel Auerbach’s Yiddish story ‘Lullaby’ (1952), which takes place in Israel, also bears out Lang’s observation about the link between the desire for justice and preserving the memory of the Holocaust by survivors and refugees who try to overcome trauma and rebuild their life. Auerbach immigrated to Israel from Europe in 1950. She was one of the chroniclers of the Warsaw ghetto. She founded and directed the testimonial collection department of the newly created Yad Vashem, where ordinary people, rather than historians and politicians, would be able to testify in their own way and words. Auerbach understood memory as an act of overcoming destruction and death through the spiritual effort involved in testifying. In Auerbach’s ‘Lullaby’, the protagonist visits her cousin Reuven, who lost his only daughter, Yosima, a pianist and composer who died in the ghetto. Reuven’s first wife could not bear the loss and took her own life. Later, Reuven became acquainted with Ruth, and they married in Israel. The narrator visits their home with one room dedicated to the memory of Yosima, and the two young children born in Israel: a girl, and a boy with the strange name Kamy, short for Nekamyah (‘God will avenge’).
Vengeance is a human emotion – not an alien element, but rather a part of modern Jewish culture
Reuven and Ruth compose lullabies to Kamy and give different meanings to the name. The father’s lullaby is:
Black crows
Tore your sister
In the black exile.
Black is the diaspora, my son.
At dawn, the sun rises,
A sun of freedom,
And remember, vengeance, my son:
Revenge!
The mother’s lullaby is:
Sleep, sleep my precious child,
Be strong, upright,
With people and with God
For the sake of father,
For the sake of mother,
For the sake of all Israel.
The narrator listens to the two lullabies and reflects on what will become of the child when he grows up. ‘Perhaps he will be a poet, perhaps an actor – someone extraordinary? And perhaps he will be an ordinary person like all others?’ Auerbach’s deceptively simple story is about a specific dilemma of Jews trying to rebuild their life after the Holocaust in Israel. It raises larger philosophical and ethical questions about personal and collective memory, trauma, revenge, justice and the meaning of being human – an ‘ordinary person’ – in dark times, a question that still haunts us today as it did after the Holocaust.
What can we learn from this story and, in general, from the literary cultural analysis I presented here? First, we must acknowledge that vengeance is a human emotion, and it is inescapable – not an alien element, but rather a part of modern Jewish culture. Second, vengeance may lead to collective memory as well as to a cycle of bloodshed. We observed the historical displacement of a desire for vengeance against Nazi Germans, mostly expressed in Yiddish during and after the Second World War, for revenge against Palestinian Arabs, mostly expressed in Hebrew and in Israel around and after 1948. This displacement has existed ever since then and has played an important role in the conflict between Israelis and Palestinians. It was activated most forcefully on 7 October 2023, because of the unprecedented violence of the attack on southern Israel, and the extreme vulnerability of Israeli Jews who sensed that the State of Israel and its army failed in its most basic function, to defend its citizens. This activation of vulnerability is, in no small part, due to the intergenerational collective trauma of the experience of the Holocaust. Because of the displacement of modern Jewish vengeance from Europe onto the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the vengeful war taking place since 7 October is even more dangerous and tragic. To begin imagining a better future for both Israelis and Palestinians, it is imperative to be more aware of this cultural history with its memories, traumas and numerous blind spots.
An earlier version of this article was published in Hebrew in Hazman Hazeh.