We are restless even in death. Entombed in stone, our most distant ancestors still travel along Earth’s subterranean passageways. One of them, a man in his 20s, began his journey around 230,000 years ago after collapsing into marshland on the lush edge of a river delta feeding a vast lake in East Africa’s Rift Valley. He became the earth in which he lay as nutrients leached from his body and his bone mineralised into fossil. Buried in the sediment of the Rift, he moved as the earth moved: gradually, inexorably.
Millions of years before he died, tectonic processes began pushing the Rift Valley up and apart, like a mighty inhalation inflating the ribcage of the African continent. The force of it peeled apart a 4,000-mile fissure in Earth’s crust. As geological movements continued, and the rift grew, the land became pallbearer, lifting and carrying our ancestor away to Omo-Kibish in southern Ethiopia where, in 1967, a team of Kenyan archaeologists led by Richard Leakey disinterred his shattered remains from an eroding rock bank.
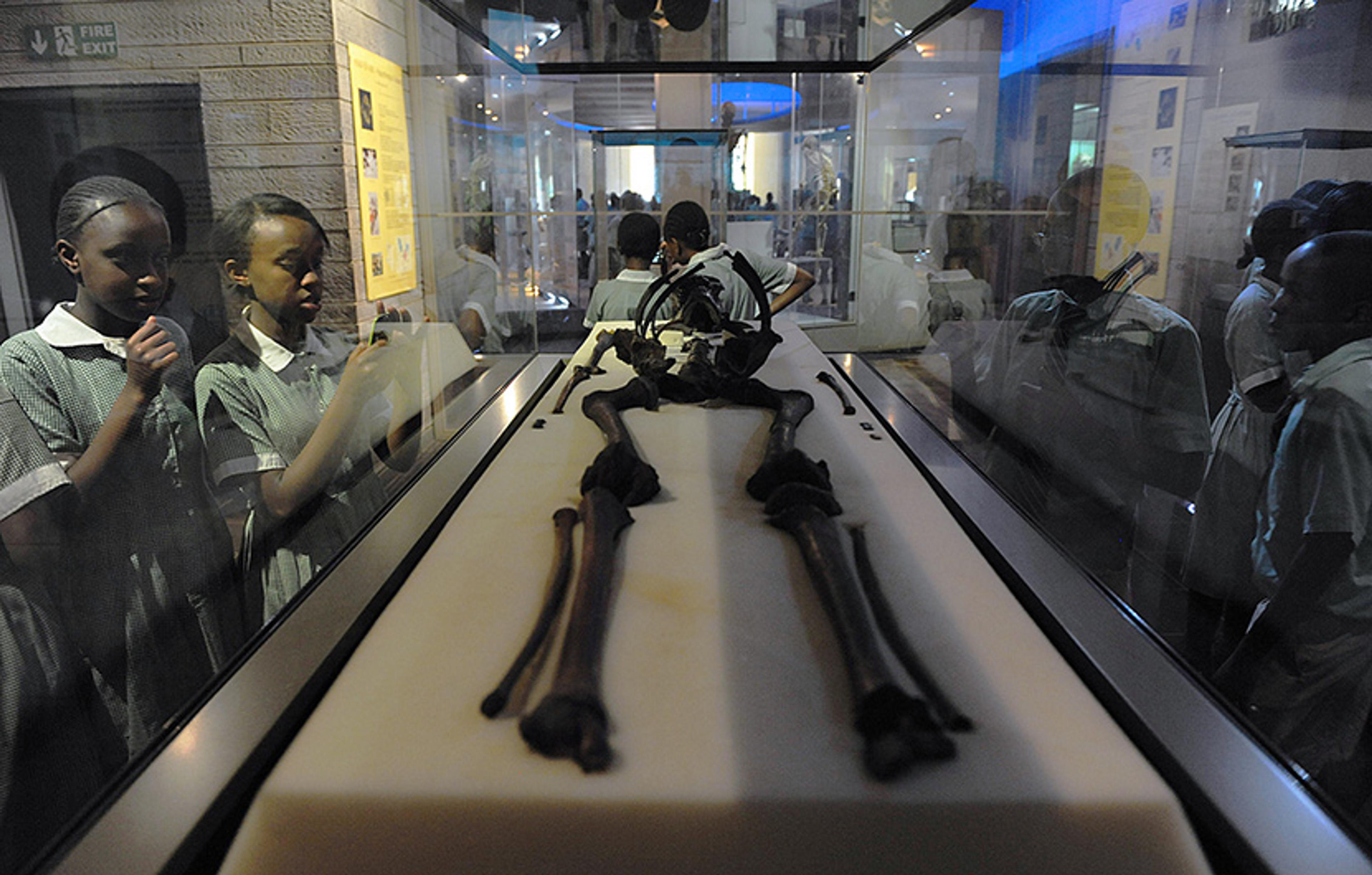
Lifted from the ground, the man became the earliest anatomically modern human, and the start of a new branch – Homo sapiens – on the tangled family tree of humanity that first sprouted 4 million years ago. Unearthed, he emerged into the same air and the same sunlight, the same crested larks greeting the same rising sun, the same swifts darting through the same acacia trees. But it was a different world, too: the nearby lake had retreated hundreds of miles, the delta had long since narrowed to a river, the spreading wetland had become parched scrub. His partial skull, named Omo 1, now resides in a recessed display case at Kenya’s national museum in Nairobi, near the edge of that immense fault line.
I don’t remember exactly when I first learned about the Rift Valley. I recall knowing almost nothing of it when I opened an atlas one day and saw, spread across two colourful pages, a large topographical map of the African continent. Toward the eastern edge of the landmass, a line of mountains, valleys and lakes – the products of the Rift – drew my eye and drove my imagination, more surely than either the yellow expanse of the Sahara or the green immensity of the Congo. Rainforests and deserts appeared uncomplicated, placid swathes of land in comparison with the fragmenting, shattering fissures of the Rift.
On a map, you can trace the valley’s path from the tropical coastal lowlands of Mozambique to the Red Sea shores of the Arabian Peninsula. It heads due north, up the length of Lake Malawi, before splitting. The western branch takes a left turn, carving a scythe-shaped crescent of deep lake-filled valleys – Tanganyika, Kivu, Edward – that form natural borders between the Democratic Republic of Congo and a succession of eastern neighbours: Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda. But the western branch peters out, becoming the broad shallow valley of the White Nile before dissipating in the Sudd, a vast swamp in South Sudan.
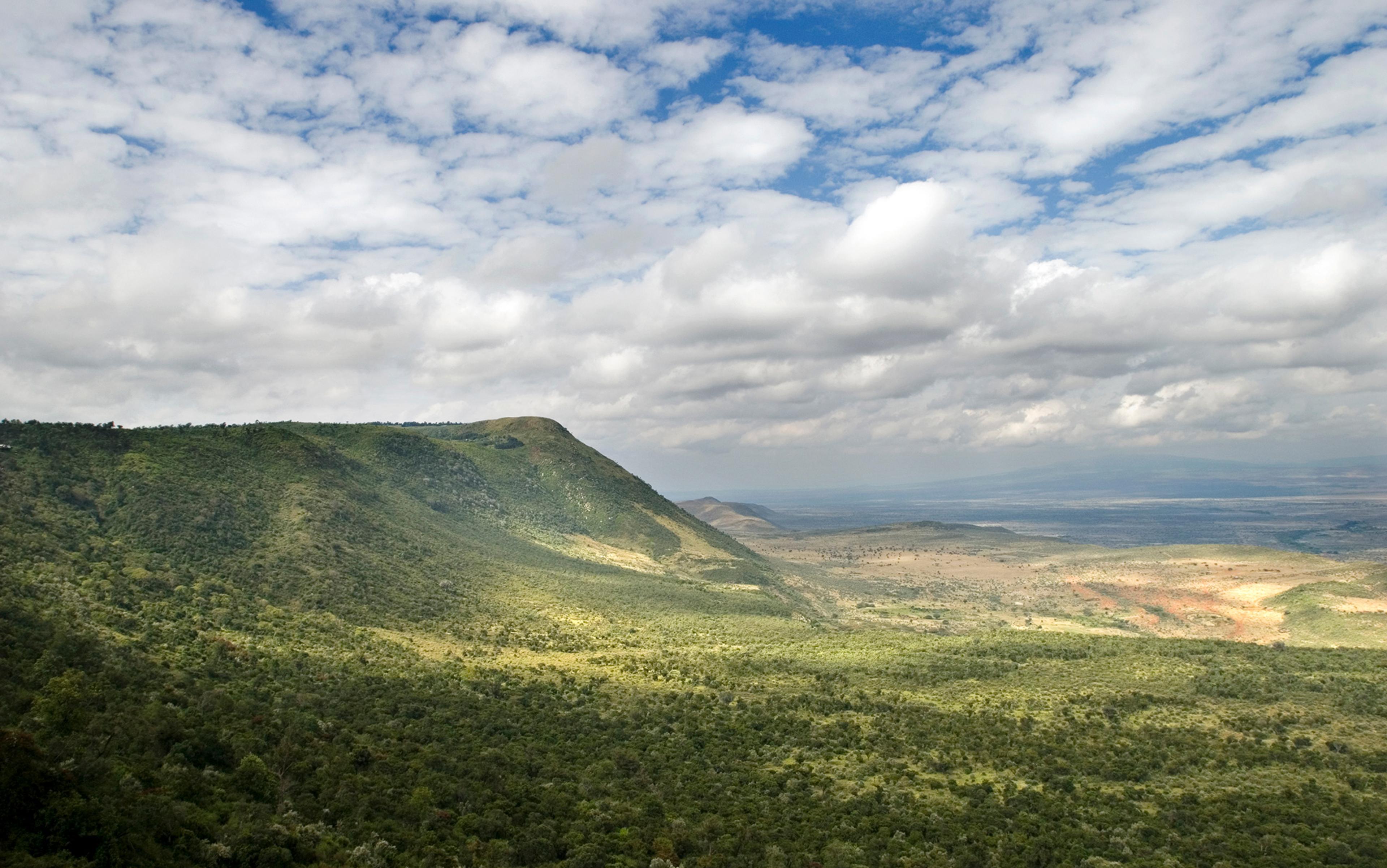
The eastern branch is more determined in its northward march. A hanging valley between steep ridges, it runs through the centre of Tanzania, weaving its way across Kenya and into Ethiopia where, in the northern Afar region, it splits again at what geologists call a ‘triple junction’, the point where three tectonic plates meet or, in this case, bid farewell. The Nubian and Somalian plates are pulling apart and both are pulling away from the Arabian plate to their north, deepening and widening the Rift Valley as they unzip the African continent. Here in the Rift, our origins and that of the land are uniquely entwined. Understanding this connection demands more than a bird’s-eye view of the continent.
The Rift Valley is the only place where human history can be seen in its entirety
Looking out across a landscape such as East Africa’s Rift Valley reveals a view of beauty and scale. But this way of seeing, however breath-taking, will only ever be a snapshot of the present, a static moment in time. Another way of looking comes from tipping your perspective 90 degrees, from the horizontal plane to the vertical axis, a shift from space to time, from geography to stratigraphy, which allows us to see the Rift in all its dizzying, vertiginous complexity. Here, among seemingly unending geological strata, we can gaze into what the natural philosopher John Playfair called ‘the abyss of time’, a description he made after he, James Hall and James Hutton in 1788 observed layered geological aeons in the rocky outcrops of Scotland’s Siccar Point – a revelation that would eventually lead Hutton to become the founder of modern geology. In the Rift Valley, this vertical, tilted way of seeing is all the more powerful because the story of the Rift is the story of all of us, our past, our present, and our future. It’s a landscape that offers a diachronous view of humanity that is essential to make sense of the Anthropocene, the putative geological epoch in which humans are understood to be a planetary force with Promethean powers of world-making and transformation.
The Rift Valley humbles us. It punctures the transcendent grandiosity of human exceptionalism by returning us to a specific time and a particular place: to the birth of our species. Here, we are confronted with a kind of homecoming as we discern our origins among rock, bones and dust. The Rift Valley is the only place where human history can be seen in its entirety, the only place we have perpetually inhabited, from our first faltering bipedal steps to the present day, when the planetary impacts of climatic changes and population growth can be keenly felt in the equatorial heat, in drought and floods, and in the chaotic urbanisation of fast-growing nations. The Rift is one of many frontiers in the climate crisis where we can witness a tangling of causes and effects.
But locating ourselves here, within Earth’s processes, and understanding ourselves as part of them, is more than just a way of seeing. It is a way of challenging the kind of short-term, atemporal, election-cycle thinking that is failing to deliver us from the climate and biodiversity crises. It allows us to conceive of our current moment not as an endpoint but as the culmination of millions of years of prior events, the fleeting staging point for what will come next, and echo for millennia to come. We exist on a continuum: a sliver in a sediment core bored out of the earth, a plot point in an unfolding narrative, of which we are both author and character. It brings the impact of what we do now into focus, allowing facts about atmospheric carbon or sea level rises to resolve as our present responsibilities.
The Rift is a place, but ‘rift’ is also a word. It’s a noun for splits in things or relationships, a geological term for the result of a process in which Earth shifts, and it’s a verb apt to describe our current connection to the planet: alienation, separation, breakdown. The Rift offers us another way of thinking.
That we come from the earth and return to it is not a burial metaphor but a fact. Geological processes create particular landforms that generate particular environments and support particular kinds of life. In a literal sense, the earth made us. The hominin fossils scattered through the Rift Valley are anthropological evidence but also confronting artefacts. Made of rock not bone, they are familiar yet unexpected, turning up in strange places, emerging from the dirt weirdly heavy, as if burdened with the physical weight of time. They are caught up in our ‘origin stories and endgames’, writes the geographer Kathryn Yusoff, as simultaneous manifestations of mortality and immortality. They embody both the vanishing brevity of an individual life and the near-eternity of a mineralised ‘geologic life’, once – as the philosopher Manuel DeLanda puts it in A Thousand Years of Nonlinear History (1997) – bodies and bones cross ‘the threshold back into the world of rocks’. There is fear in this, but hope too, because we can neither measure, contend with, nor understand the Anthropocene without embedding ourselves in different timescales and grounding ourselves in the earth. Hominin fossils are a path to both.
The rain, wind and tectonics summon long-buried bones, skulls and teeth from the earth
Those species that cannot adapt, die. Humans, it turns out – fortunately for us, less so for the planet – are expert adapters. We had to be, because the Rift Valley in which we were born is a complex, fragmented, shifting place, so diverse in habitats that it seems to contain the world. It is as varied as it is immense, so broad that on all but the clearest of days its edges are lost in haze. From high on its eastern shoulder, successive hills descend thousands of feet to the plains below, like ridges of shoreward ocean swell. Here, the valley floor is hard-baked dirt, the hot air summoning dust devils to dance among whistling thorns, camphor and silver-leafed myrrh. Dormant volcanoes puncture the land, their ragged, uneven craters stark against the sky. Fissures snake across the earth. Valley basins are filled with vast lakes, or dried out and clogged with sand and sediment. An ice-capped mountain stands sentinel, its razor ridges of black basalt rearing out of cloud forest. Elsewhere, patches of woodland cluster on sky islands, or carpet hills and plateaus. In some of the world’s least hospitable lands, the rain, wind and tectonics summon long-buried bones, skulls and teeth from the earth. This is restless territory, a landscape of tumult and movement, and the birthplace of us all.
My forays into this territory over the past dozen years have only scratched at the surface of its immense variety. I have travelled to blistering basalt hillsides, damp old-growth forests, ancient volcanoes with razor rims, smoking geothermal vents, hardened fields of lava, eroding sandstone landscapes that spill fossils, lakes with water that is salty and warm, desert dunes with dizzying escarpments, gently wooded savannah, and rivers as clear as gin. Here, you can travel through ecosystems and landscapes, but also through time
I used to live beside the Rift. For many years, my Nairobi home was 30 kilometres from the clenched knuckles of the Valley’s Ngong Hills, which slope downwards to meet a broad, flat ridge. Here, the road out of the city makes a sharp turn to the right, pitching over the escarpment’s edge before weaving its way, thousands of feet downwards over dozens of kilometres, through patchy pasture and whistling thorns. The weather is always unsettled here and, at 6,500 feet can be cold even on the clearest and brightest of days.
One particularly chilly bend in the road has been given the name ‘Corner Baridi’, cold corner. Occasionally, I would sit here, on scrubby grass by the crumbling edge of a ribbon of old tarmac, and look westwards across a transect of the Rift Valley as young herders wandered past, bells jangling at their goats’ necks. The view was always spectacular, never tired: a giant’s staircase of descending bluffs, steep, rocky and wooded, volcanic peaks and ridges, the sheen of Lake Magadi, a smudge of smoke above Ol Doinyo Lengai’s active caldera, the mirrored surface of Lake Natron, the undulating expanse of the valley floor.
And the feeling the scene conjured was always the same: awe, and nostalgia, in its original sense of a longing for home, a knowledge rooted in bone not books. This is where Homo sapiens are from. This is fundamental terrane, where all our stories begin. Sitting, I would picture the landscape as a time-lapse film, changing over millions of years with spectral life drifting across its shifting surface like smoke.
Humankind was forged in the tectonic crucible of the Rift Valley. The physical and cognitive advances that led to Homo sapiens were driven by changes of topography and climate right here, as Earth tipped on its axis and its surface roiled with volcanism, creating a complex, fragmented environment that demanded a creative, problem-solving creature.
Much of what we know of human evolution in the Rift Valley builds on the fossil finds and theoretical thinking of Richard Leakey, the renowned Kenyan palaeoanthropologist. Over the years I lived in Nairobi, we met and talked on various occasions and, one day in 2021, I visited him at his home, a few miles from Corner Baridi.
Millennia from now, the Rift Valley will have torn the landmass apart and become the floor of a new sea
It was a damp, chilly morning and, when I arrived, Leakey was finishing some toast with jam. Halved red grapefruit and a pot of stovetop espresso coffee sat on the Lazy Susan, a clutch bag stuffed with pills and tubes of Deep Heat and arthritis gel lay on the table among the breakfast debris, a walking stick hung from the doorknob behind him, and from the cuffs of his safari shorts extended two metal prosthetic legs, ending in a pair of brown leather shoes.
At the time, the 77-year-old had shown a knack for immortality, surviving the plane crash that took his legs in 1993, as well as bouts of skin cancer, transplants of his liver and kidneys, and COVID-19. He died in January 2022, but he was as energetic and enthused as I had ever seen him when we met. We discussed Nairobi weather, Kenyan politics, pandemic lockdowns, and his ongoing work. He described his ambitions for a £50 million museum of humankind, to be called Ngaren (meaning ‘the beginning’, in the Turkana language) and built close to his home on a patch of family land he planned to donate. It was the only place that made sense for the museum, he said, describing how the fossils he had uncovered over the years – among them, Omo 1 and the Homo erectus nicknamed Turkana Boy – were all phrases, sentences, or sometimes whole chapters in the story of where we came from, and who we are. ‘The magic of the Rift Valley is it’s the only place you can read the book,’ he told me.

Afterwards, I drove out to the spot where Leakey envisioned his museum being built: a dramatic basalt outcropping amid knee-high grass and claw-branched acacias, perched at the end of a ridge, the land falling precipitously away on three sides. It felt like an immense pulpit or perhaps, given Leakey’s paternal, didactic style, atheist beliefs, and academic rigour, a lectern.
A little way north of Leakey’s home, beyond Corner Baridi, a new railway tunnel burrows through the Ngong Hills to the foot of the escarpment where there is a town of low-slung concrete, and unfinished roofs punctured by reinforced steel bars. For most hours of most days, lorries rumble by, nose to tail, belching smoke and leaking oil. They ferry goods back and forth across the valley plains. The new railway will do the same, moving more stuff, more quickly. The railway, like the road, is indifferent to its surroundings, its berms, bridges, cuttings and tunnels defy topography, mock geography.
Running perpendicular to these transport arteries, pylons stride across the landscape, bringing electricity in high voltage lines from a wind farm in the far north to a new relay station at the foot of a dormant volcano. The promise of all this infrastructure increases the land’s value and, where once there were open plains, now there are fences, For Sale signs, and quarter-acre plots sold in their hundreds. Occasionally, geology intervenes, as it did early one March morning in 2018 when Eliud Njoroge Mbugua’s home disappeared.
It began with a feathering crack scurrying across his cement floor, which widened as the hours passed. Then the crack became a fissure, and eventually split his cinderblock shack apart, hauling its tin-roofed remnants into the depths. Close by, the highway was also torn in two. The next day, journalists launched drones into the sky capturing footage that revealed a lightning-bolt crack in the earth stretching hundreds of metres across the flat valley floor. Breathless news reports followed, mangling the science and making out that an apocalyptic splitting of the African continent was underway. They were half-right.
Ten thousand millennia from now, the Rift Valley will have torn the landmass apart and become the floor of a new sea. Where the reports were wrong, however, was in failing to recognise that Mbugua’s home had fallen victim to old tectonics, not new ones: heavy rains had washed away the compacted sediment on which his home had been built, revealing a fault line hidden below the surface. Sometimes, the changes here can point us forward in time, toward our endings. But more often, they point backwards.
Just a few years earlier, when I first moved to Nairobi, the railway line and pylons did not exist. Such is the velocity of change that, a generation ago, the nearby hardscrabble truck stop town of Mai Mahiu also did not exist. If we go four generations back, there were neither trucks nor the roads to carry them, neither fence posts nor brick homes. The land may look empty in this imagined past, but is not: pastoralist herders graze their cows, moving in search of grass and water for their cattle, sharing the valley with herds of elephant, giraffe and antelope, and the lions that stalk them.
Thousands of years earlier still, and the herders are gone, too. Their forebears are more than 1,000 miles to the northwest, grazing their herds on pastures that will become the Sahara as temperatures rise in the millennia following the end of the ice age, the great northern glaciers retreat and humidity falls, parching the African land. Instead, the valley is home to hunter-gatherers and fishermen who tread the land with a lighter foot.
Go further. At the dawn of the Holocene – the warm interglacial period that began 12,000 years ago and may be coming to a close – the Rift is different, filled with forests of cedar, yellowwood and olive, sedge in the understory. The temperature is cooler, the climate wetter. Dispersed communities of human hunter-gatherers, semi-nomads, live together, surviving on berries, grasses and meat, cooking with fire, hunting with sharpened stone. Others of us have already left during the preceding 40,000 years, moving north up the Rift to colonise what will come to be called the Middle East, Europe, Asia, the Americas.
As geology remakes the land, climate makes its power felt too, swinging between humidity and aridity
Some 200,000 years ago, the Rift is inhabited by the earliest creature that is undoubtedly us: the first Homo sapiens, like our ancestor found in Ethiopia. Scrubbed and dressed, he would not turn heads on the streets of modern-day Nairobi, London or New York. At this time, our ancestors are here, and only here: in the Rift.
Two million years ago, we are not alone. There are at least two species of our Homo genus sharing the Rift with the more ape-like, thicker-skulled and less dexterous members of the hominin family: Australopithecus and Paranthropus. A million years earlier, a small, ape-like Australopithecus (whom archaeologists will one day name ‘Lucy’) lopes about on two legs through a mid-Pliocene world that is even less recognisable, full of megafauna, forests and vast lakes.
Further still – rewinding into the deep time of geology and tectonics, through the Pliocene and Miocene – there is nothing we could call ‘us’ anymore. The landscape has shifted and changed. As geology remakes the land, climate makes its power felt too, swinging between humidity and aridity. Earth wobbles on its axis and spins through its orbit, bringing millennia-long periods of oscillation between wetness and dryness. The acute climate sensitivity of the equatorial valley means basin lakes become deserts, and salt pans fill with water.
On higher ground, trees and grasses engage in an endless waltz, ceding and gaining ground, as atmospheric carbon levels rise and fall, favouring one family of plant, then the other. Eventually, the Rift Valley itself is gone, closing up as Earth’s crust slumps back towards sea level and the magma beneath calms and subsides. A continent-spanning tropical forest, exuberant in its humidity, covers Africa from coast to coast. High in the branches of an immense tree sits a small ape, the common ancestor of human and chimpanzee before tectonics, celestial mechanics and climate conspire to draw us apart, beginning the long, slow process of splitting, separating, fissuring, that leads to today, tens of millions of years later, but perhaps at the same latitude and longitude of that immense tree: a degree and a half south, 36.5 degrees west, on a patch of scrubby grass at the edge of the Rift.